The Intersection of Cat and Dog: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
For generations, people have been intrigued by the way cats and dogs relate to one another. Often kept under the same roof, these two species have become cherished companions in countless homes. This overview explores how they interact, where they converge and diverge, and the influence they exert on everyday life. By surveying their shared experiences, we gain insight into the distinctive bond that continues to shape human households.
The Evolutionary Connection
Evolutionary Background
Cats and dogs trace back to a distant common ancestor, branching off on separate paths millions of years ago. While each lineage later occupied its own ecological niche, that shared heritage still surfaces in certain behaviors and physical traits.

Domestication and Human Interaction
Both species entered human society through independent domestication events. Dogs were first welcomed as helpers thousands of years ago, followed somewhat later by cats attracted to settled communities. Over time, people and pets developed a mutually supportive partnership that endures today.
Interactions and Social Dynamics
Companionship and Bonding
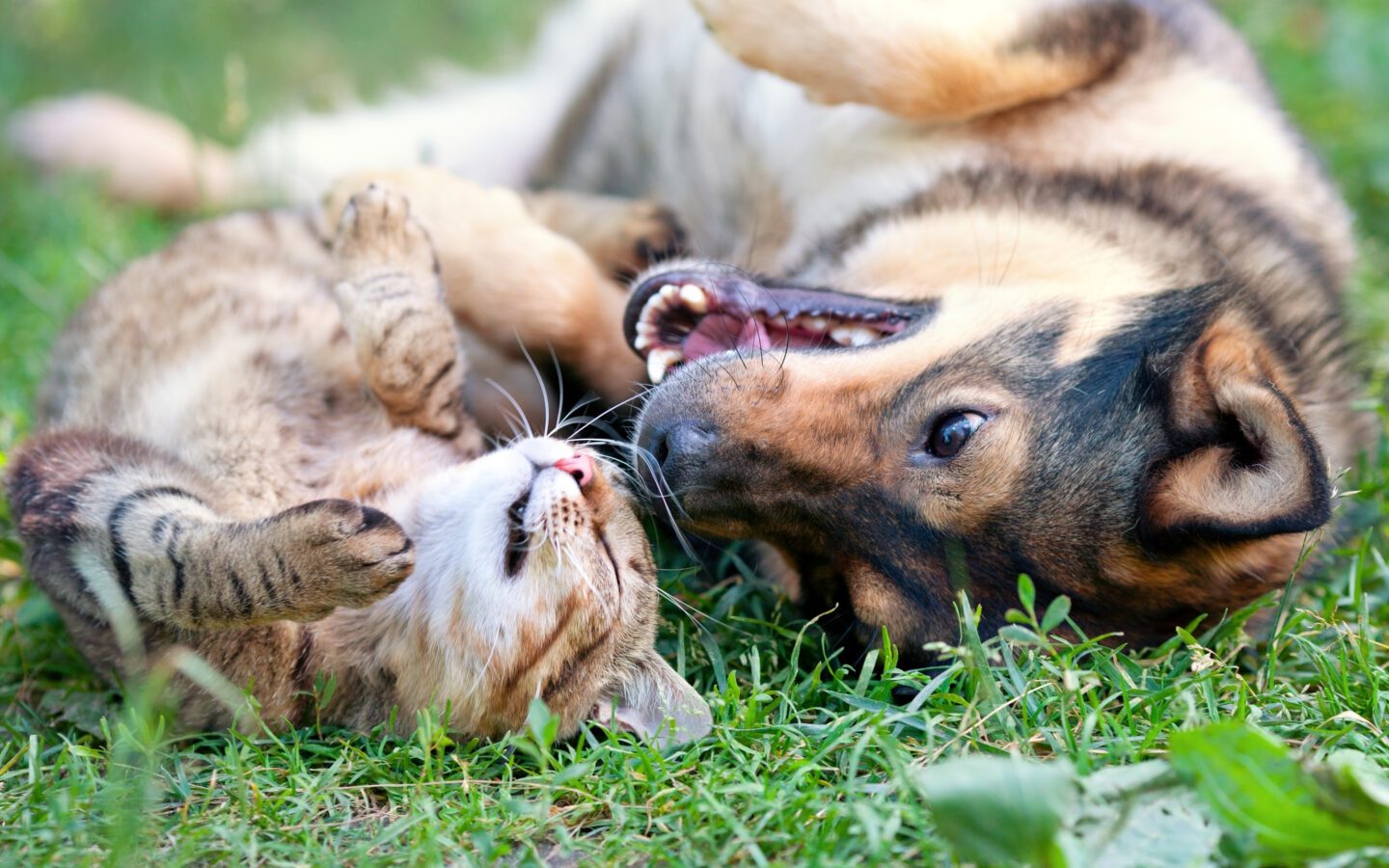
Although popular culture often portrays them as rivals, many cats and dogs form gentle, lasting friendships. Under the right conditions they share resting spots, play quietly, and appear to offer one another comfort, illustrating that affection can cross species lines.
Communication and Social Behavior
Dogs tend to broadcast their feelings through exuberant body language and varied vocal cues, whereas cats rely on subtle posture shifts and softer sounds. Despite these stylistic differences, individuals of both kinds can learn to read one another, reducing tension and encouraging peaceful coexistence.
Similarities and Differences
Similarities in Behavior
Both animals are capable of forming strong social attachments, not only with people but also with other pets. Play, exploration, grooming, and displays of emotion such as excitement or caution can be observed in each species.
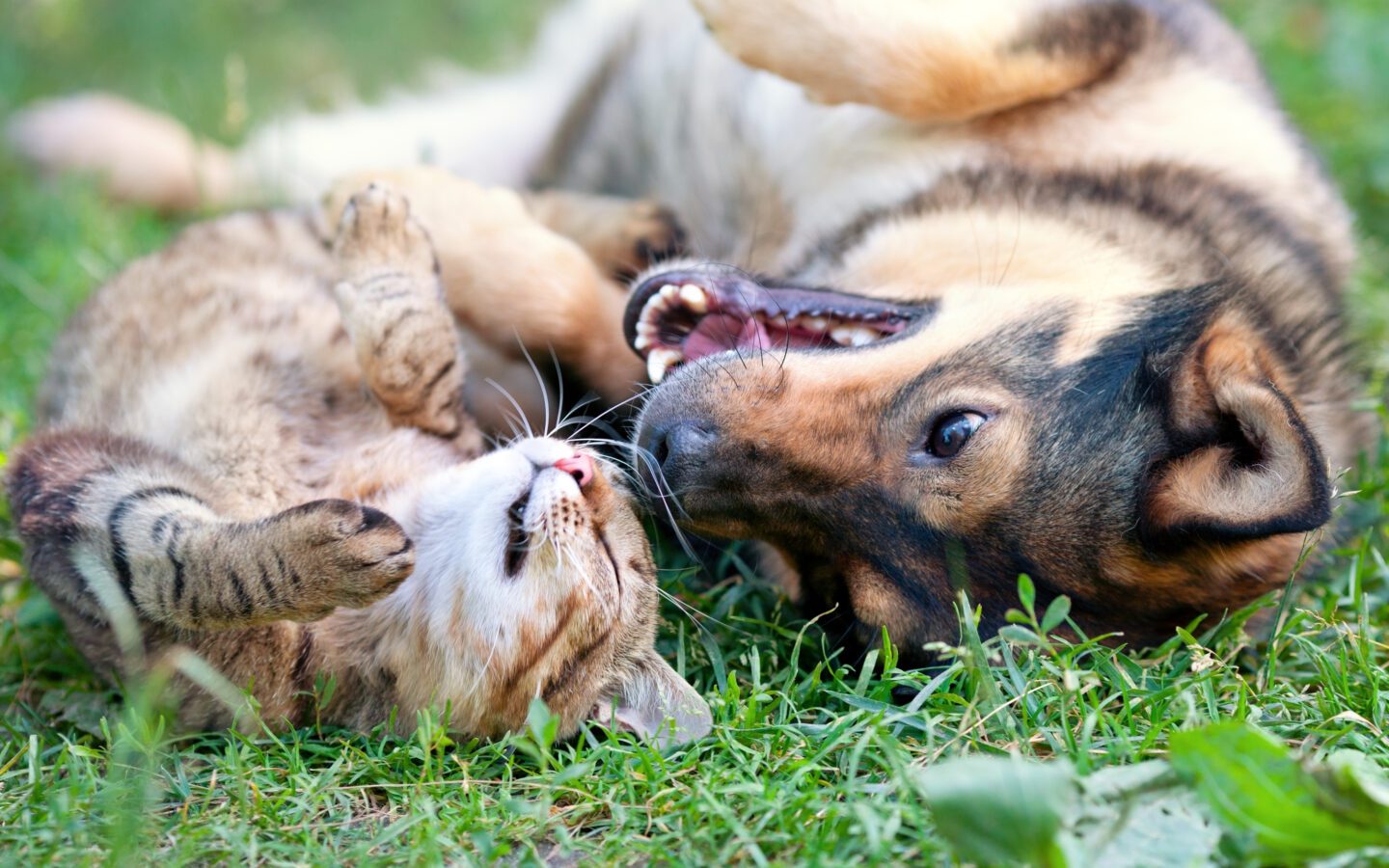

Differences in Temperament
Dogs often seek group interaction and direction, while cats frequently value autonomy and careful observation. These contrasting preferences shape how they share space and negotiate daily routines.
Impact on Human Society
Psychological Benefits
Sharing life with a pet is linked to reduced stress and improved mood. The simple acts of stroking fur, enjoying quiet company, or engaging in play can foster calm and encourage healthy routines.
Societal Impact
Beyond the home, cats and dogs inspire art, literature, and community events, while the broader pet sector supports services ranging from healthcare to recreation. Their symbolic roles as guardians, companions, and sources of joy continue to influence cultures worldwide.
Conclusion
The interplay between cats and dogs is both nuanced and rewarding. Recognizing their evolutionary roots, individual personalities, and collective influence on human well-being allows us to appreciate the quiet harmony that can flourish when whiskers meet wagging tails.
Recommendations and Future Research
To expand our knowledge of inter-species relationships among companion animals, the following avenues merit attention:
1. Comparative studies on learning styles and problem-solving strategies in household cats and dogs.
2. Exploration of hereditary factors that affect sociability and adaptability.
3. Examination of early socialization practices that foster friendly encounters between the two species.
4. Continued investigation into the emotional and physical health benefits of multi-pet households.
Pursuing these lines of inquiry will refine best practices for caregivers and enhance quality of life for both people and their animal companions.